
In this example i will generate keys with 4096 bit size You can also specify the number of bits to be used for the keys by using -b In this example I am creating key pair of ED25519 typeīy default ssh-keygen generates SSH key with 2048 bit size.Use -t argument to define the type of the key.You can create key with dsa, ecdsa, ed25519, or rsa type.By default ssh-keygen will create RSA type key.Snippet from my terminal Generate SSH Key without any arguments Next provided the passphrase, you can just press ENTER to create passphrase less key pair.The default naming syntax used for the private RSA key will be id_rsa and public key will be id_rsa.pub.The tool will create ~/.ssh if the directory does not exists already.The default location would be inside user's home folder under.The tool will prompt for the location to store the RSA key pairs.You can execute ssh-keygen without any arguments which will generate key pairs by default using RSA algorithm.Let us explore the ssh-keygen tool to generate different types of key pairs in Linuxġ. If you forgot the passphrase then there is no way to reset the passphrase and you must recreate new passphrase and place they key pairs at respective locations to re-activate public key authentication.If you wish to use SSH with public key authentication then use this once to create the authentication key in ~/.ssh/id_dsa, ~/.ssh/id_ecdsa, ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 or ~/.ssh/id_rsa.This tool supports different arguments which can be used to create keys as per the requirement.
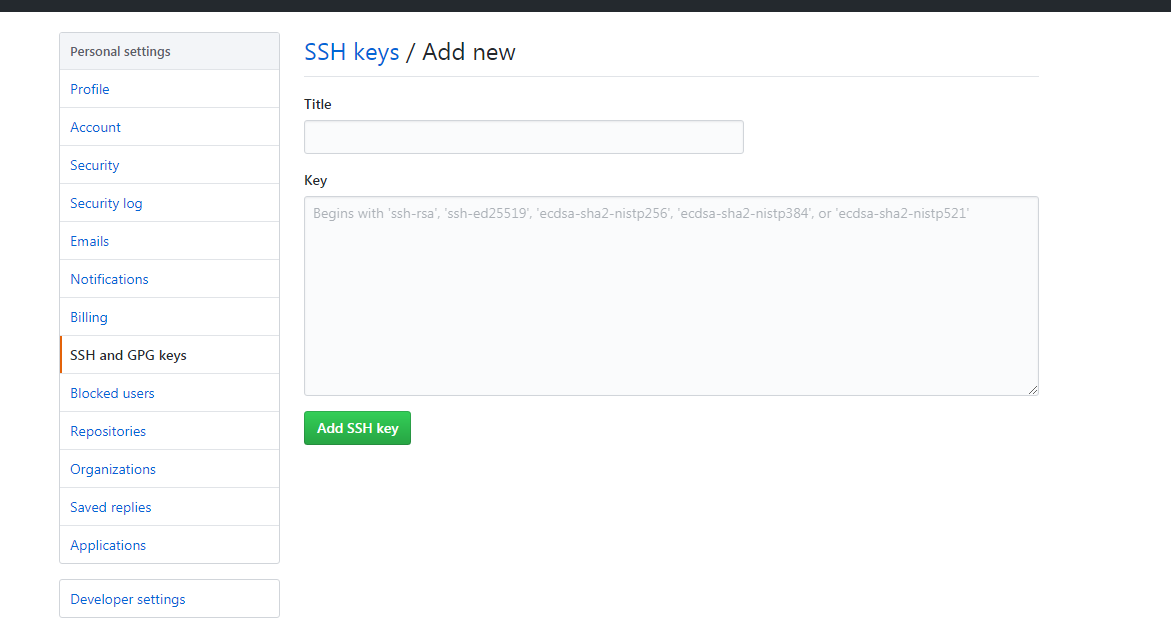
anything.pub is the public key, which you could append to the user's ~/.ssh/authorized_keys on any destination server.
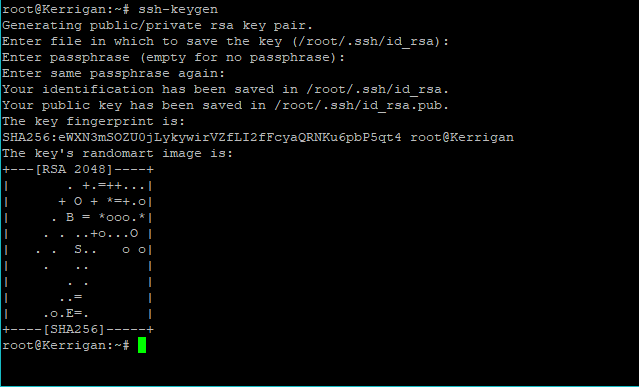
Ssh-keygen -f anything creates two files in the current directory.

Or even safer, as the user is not likely to be required to change it upon first login. You could do that with ssh-keygen, however, remember that the private key is meant to be private to the user so you should be very careful to keep it safe- as safe as the user's password.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
